WDM-PON technology implementation and its 5G bearer application scenarios and significance
Advanced technology plays a crucial role in shaping the future of communication networks, especially with the rise of 5G. One of the key technologies that support 5G is WDM-PON (Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network), which is designed to meet the demands of various 5G application scenarios.
1. WDM-PON and 5G Application Scenarios
With the rapid development of mobile internet and the emergence of new applications like the Internet of Things (IoT), there is an increasing need for high-speed data transmission and massive device connectivity. This has led to the development of 5G technology, which was officially defined by ITU-R in 2015 with three main application scenarios: eMBB (enhanced Mobile Broadband), mMTC (massive Machine Type Communication), and URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication). Each scenario requires different network capabilities, from high bandwidth for video streaming to ultra-low latency for autonomous driving and industrial automation.
In response to these needs, China Mobile released a white paper on 5G C-RAN requirements in 2016. The BBU (Baseband Unit) was restructured into two functional entities: CU (Centralized Unit) and DU (Distributed Unit). This architecture allows for more flexible deployment and better resource management, supporting both centralized and distributed operations.
The two-stage pre-transmission C-RAN architecture provides support for DU and CU pooling. The first stage, Fronthaul, supports protocols such as eCPRI, while the second stage, Midhaul, handles higher-level functions. These stages have different latency and bandwidth requirements depending on the 5G service being supported.
2. WDM-PON Technology and Its Role in 5G
WDM-PON is a promising solution for 5G pre-transmission due to its ability to support high bandwidth, low latency, and efficient resource utilization. It can be used to connect 5G DUs and BBUs through a passive optical network, enabling efficient mobile service delivery.
Key technologies in WDM-PON include colorless ONU (Optical Network Unit) technology and auxiliary management channel (AMCC) technology. Colorless ONUs allow for flexible wavelength allocation, while AMCC enables efficient management of the network without requiring additional resources.
WDM-PON offers several advantages for 5G deployment, including reduced fiber usage, improved transmission efficiency, and cost savings. It also supports the integration of wired and wireless access, paving the way for future fixed-mobile convergence networks.
3. Standards and Operator Adoption
Currently, WDM-PON standards focus on systems with single wavelengths below 10G. However, with the growing demand for higher data rates, there is increasing interest in 25G WDM-PON systems. International operators such as Deutsche Telekom, Telstra, and China Telecom are actively exploring the use of WDM-PON for 5G pre-transmission and are conducting trials and tests to evaluate its performance.
As 5G continues to evolve, WDM-PON is expected to play a vital role in enabling efficient, scalable, and cost-effective network infrastructure. With ongoing standardization efforts and operator adoption, it is set to become a key component of next-generation communication networks.
Cylindrical lens are offered in both plano-concave and plano-convex configurations, they are typically used to focus incoming light to a line, or to change the aspect ratio of an image. Cylinder Lenses are available with positive or negative focal lengths, they are used for the optics, lasers, medical science, electronics, tele-communication and others.
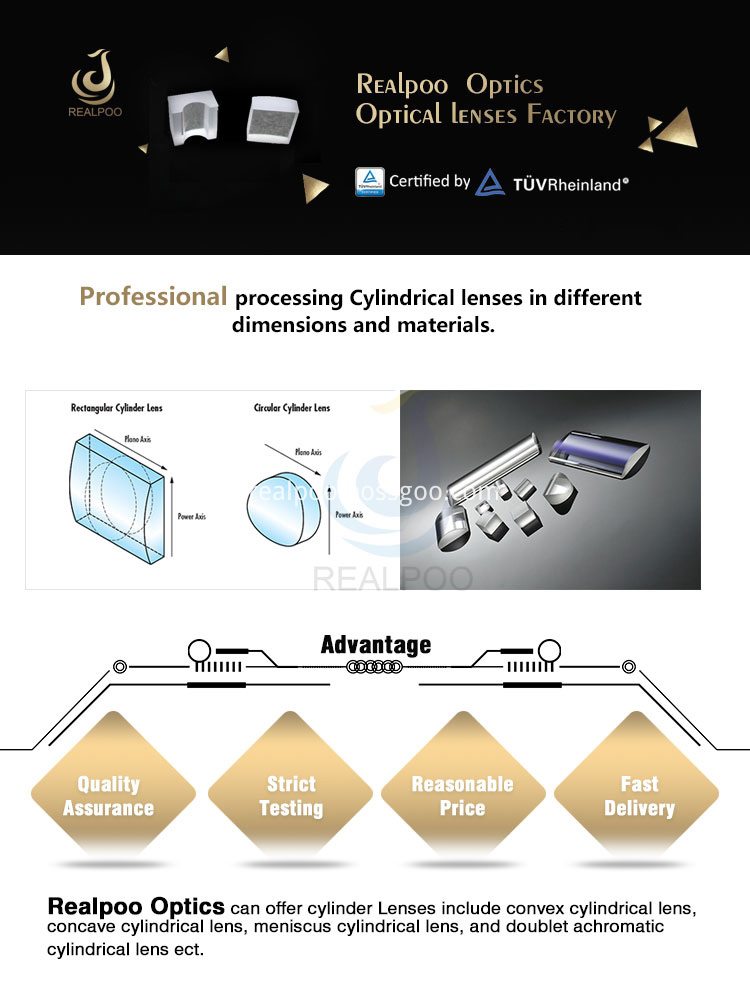


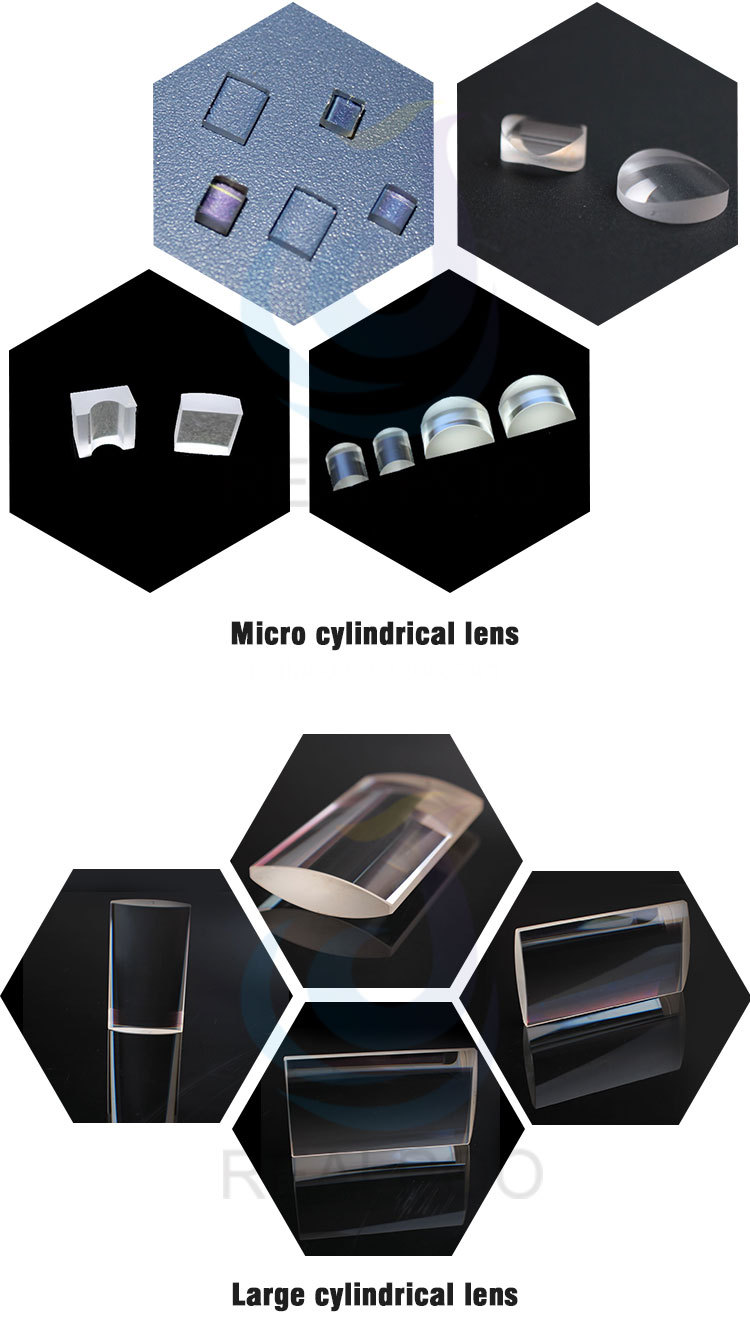


Cylindrical lenses,Positive cylindrical lenses, Line Light,Laser Focusing Lenses,Negtive cylindrical lenses
Changchun Realpoo Photoelectric Co., Ltd. , https://www.optics-realpoo.com