Detailed description of various new brake control systems
In order to improve the safety of the car, in addition to the standard configuration of ABS, some new brake control systems are still being introduced. Such as electronic brake force distribution system EBD (Electronic Braking Force Distribution), curve brake control system CBC (Curve Braking Control), brake assist system BAS (Braking Assistant System) and electric control system EBS (Electronic Braking System) .
This article refers to the address: http://
1. Electronic Brake Force Distribution System (EBD)
The braking force of the car can only be less than or equal to the adhesion of the wheel to the ground. In the case where the adhesion conditions permit, it is desirable that the braking force is as large as possible to minimize the braking distance. However, when the braking force is equal to the adhesion, so that the wheel locks and slips, the brake can not receive the expected effect. If the front wheel brakes and the rear wheel is still rolling, the car will lose its steering control ability due to the steering wheel locking and losing lateral adhesion. If the rear wheel brakes and the front wheel still rotates, the car may be tailed or even turned around with a small lateral force. The latter has a more serious traffic accident than the former. Therefore, in order to obtain the greatest possible braking force and the stability of the holding direction, that is, neither the steering control ability nor the tail or even the head turning, the front and rear wheel brakes should reach the lock slip simultaneously. The condition that the front and rear wheels are synchronously locked and slipped is that the ratio of the braking forces of the front and rear wheels should be equal to the ratio of the vertical loads of the front and rear wheels to the road surface.
When the car is braked, the vertical load on the ground from the front wheels will increase due to inertia. The greater the braking force, the greater the ratio of the front and rear wheels to the ground vertical load. If the ratio of the front and rear wheel braking forces can be adjusted to the ratio of the vertical load (or adhesion) of the front and rear wheels to the ground, the front and rear wheels of the car can be locked and slipped simultaneously. If the front and rear wheels are braking, they will reach the lock at the same time, and the braking efficiency is the highest.
When the car is empty and full load, the center of gravity is different, the total mass is different, and the ideal front and rear wheel braking force distribution ratio is also different. In order to avoid the worst case of the rear wheel lock first, and make full use of the ground adhesion conditions to generate the maximum braking force, it is necessary to adjust the braking force of the car brake system to meet the conditions of empty and heavy vehicles. The ideal braking force distribution ratio. The conventional brake system connects the mechanical brake force adjustment device in series with the rear actuation line or the front actuation line. These devices are limited pressure valves, proportional valves, incremental valves, load sensing valves, and inertia valves.
The load-sensing valve can sense the actual loading quality of the vehicle, and adjusts the pipeline pressure distribution characteristic curve according to the total mass and the center of gravity of the vehicle, so that the front and rear wheels can realize the synchronous lock slip when the empty car or the truck is braked. The function of the pressure limiting valve on the actuating line after connecting the pneumatic or hydraulic brake system is that after the current pressure or hydraulic pressure in the current actuating line reaches a certain value, the gas pressure in the actuating line is limited. Or the hydraulic pressure remains the same to prevent the rear wheel from braking and locking. The function of the proportional valve on the actuating line after connecting the pneumatic or hydraulic brake system is that after the current pressure or hydraulic pressure in the current actuating line reaches a certain value, the air pressure in the actuating line is automatically limited. Or the rate of increase of the hydraulic pressure, the rate of increase of the gas pressure or the hydraulic pressure in the actuating pipeline is lower than that of the front actuating pipeline, so that the rear wheel can also obtain the largest possible braking force and will not be earlier than the front wheel. Hug. It is only used for the incremental valve of the pneumatic brake system connected in series in the front actuating pipeline. Later, the pipeline air pressure is actuated as the control pressure. The gas pressure of the pre-actuated pipeline can be controlled to obtain the similarity and promotion of the proportional valve. Dynamic pressure distribution characteristics of the moving pipe. Inertial valve for hydraulic brake system, the action characteristic curve is similar to the load-sensing valve, but the control start point control pressure depends on the inertial force acting on the center of gravity of the car during braking, ie the starting point control pressure depends not only on the total vehicle Quality, and depends on the car brake deceleration.
The brake system in which the above mechanical brake force regulating valve is installed does not guarantee a high braking efficiency on any road surface. The car with the ABS is also installed, although it can avoid the locks of different wheels during the braking process, and it can prevent the side slip or lose the steering ability, but it does not necessarily ensure that the front and rear wheels reach the maximum braking strength at the same time. Get the shortest braking distance. On the basis of ABS, the addition of the electronic brake force distribution system EBD can effectively solve this problem.
The difference between the brake slip ratios of the front and rear wheels is:
S=S1-S2=(R2ω2−R1ω1)/υ
In the formula, S1 and S2 are the braking slip ratios of the front and rear wheels, respectively; R1, ω1 and R2, ω2 are the wheel diameter and angular velocity of the front and rear wheels, respectively; υ is the vehicle speed.
The slip ratio when the wheel is locked is S=100%. The ideal braking condition is that the front and rear wheels are locked at the same time. At this time, ΔS=0, that is, R2ω2=R1ω1. If the difference between the brake slip ratios of the front wheels and the rear wheels is always △S=0 during the braking process of the vehicle, that is, the control R2ω2=R1ω1 can ensure that the front and rear wheels simultaneously reach the locked state.
Figure 1 compares the adjustment performance of the mechanical braking force adjustment device and the braking force of the electronic brake force distribution system EBD. It can be seen that although the mechanical braking force adjustment device can avoid the rear wheel locking first, the system The power regulation performance curve differs greatly from the ideal braking force distribution curve of light and heavy vehicles, and the braking efficiency is low. The electronic braking force distribution system can produce a zigzag pressure regulation function under the condition of light vehicle or heavy vehicle, so that the braking force curve and the ideal braking force distribution curve have better fitting rate and higher braking efficiency.
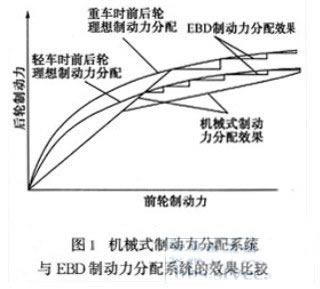
The adjustment process of the electronic brake force distribution system EBD and the adjustment process of the anti-lock brake system ABS are similar, that is, by implementing cyclic control of the wheel brake pressure, such as constant pressure reduction, pressure holding, and boosting. Therefore, electronic brake force distribution and brake anti-lock can be simultaneously achieved by modifying the control software program on a vehicle equipped with ABS. During the braking process of the car, the EBD works first, and the ABS only works when the wheel is close to lock, and the EBD function disappears. At present, domestic cars such as Santana 2000GSi, Palio, Siena, Familia, etc. are equipped with ABS ten EBD brake system.
2. Turning brake control system CBC
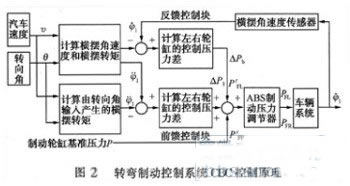
When the car turns, there is a large centrifugal force, especially when the vehicle speed is high. At this time, braking the car, not only to maintain the lateral stability of the car, but also to have a good braking effect, only ABS ten EBD is not enough. The function of the turning brake control system CBC is to obtain a larger braking force during the braking process by adjusting the brake pressure in the wheel brake wheel cylinders on both sides of the vehicle when the vehicle is turning and braking.
The turning brake control usually adopts the combined control method of steering angle feedforward (Feedforward) and yaw angular velocity feedback (Feedback). The control principle is shown in Fig. 2. In order to realize the adjustment of the brake pressure in the wheel-wheel cylinders on both sides of the car when turning, four wheel-cylinder pressure sensors, one yaw rate sensor, one car acceleration sensor and one are added to the ABS hardware. Steering angle sensor. The CBC independently controls each brake wheel to stabilize the braking process and have sufficient braking force to ensure that the car's cornering braking performance is the same as the straight-line braking performance. The BMW X4.6is utility vehicle (SUV) is equipped with a CBC system.
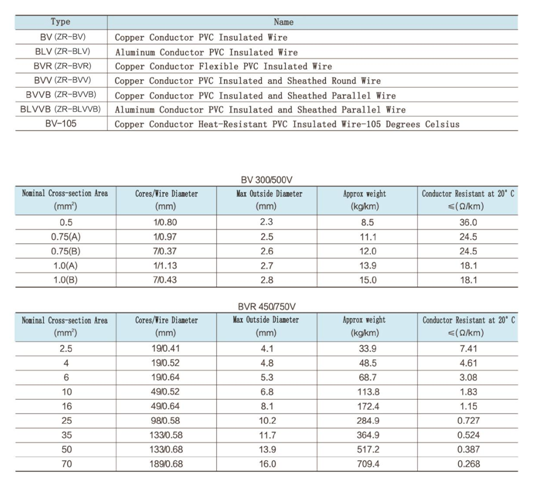
PVC insulated wires are coated with pvc to prevent from electric shock. Its light weight reduces manual handling difficulties. This wire consists of copper/aluminum conductor, insulated with moisture and heat resistant, chemically cross-linked polyethylene insulation. PVC does not conduct electricity and is therefore an excellent material to use for electrical applications such as insulation sheathing for cables. With fine design and high quality, the wire boasts of large electricity transmission capacity. The maximum continuous operating temperature for general type is 75℃. But the special type BV-105 can work well at the temperature of 105℃.
Standard:
GB/T5023-2008, JB/T 8734-2016

Rated Voltage:
450/750V

Application:
cables are extensively used for domestic home appliances wiring, house wiring and internal wiring for lighting circuits in factories, power supply for office automation, in control, instrumentation, submarine, mining, ship wiring applications etc. due to its high tensile strength, superior conductivity, better flexibility and ease of jointing.
Advantages:
- A non-hygroscopic insulation almost unaffected by moisture.
- Non-migration of compound permitting vertical installation.
- A tough and resilient sheath with excellent fire retarding quality.
- High current and short circuit current rating.
- Not affected by vibration.
- Reduce internal stress and low dielectric loss
- Complete protection against most forms of electrolytic and chemical corrosion.
- Good ageing characteristics
- Easy installation
Welcome to visit our factory to learn more about us. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
PVC Insulated Wire,Heat Resistant PVC Insulated Wires,PVC Insulator Sheath Electrical Wires,Flexible PVC Electrical Wires
Fujian Lien Technology Co.,Ltd , http://www.liencable.com