Hybrid networking of WiMAX wireless broadband network, analysis of local advantages
In recent years, as the ARPU value of voice services continues to decline, wireless broadband data services have become a new business growth point sought by operators. According to the analysis data of Cisco in 2009, in the next five years, wireless data services will show a hundredfold growth trend, with great potential. Facts have proved that the emergence of miniaturized large-screen terminals such as Laptop, UMPC, IPhone, and Smart Phone has surged the demand for unlimited broadband data services, which has caused existing 3G networks to be overwhelmed. The market needs to provide higher-speed wireless bearer networks.
WiMAX should be built on the new needs and new concepts of broadband data network constructionWiMAX has emerged as a mobile device. On the one hand, it has become a tool for emerging operators, operators in catch-up positions to rapidly deploy networks, seize market opportunities, achieve competitive transcendence and later become the weapon; on the other hand, it helps traditional large fixed-line operators to retain and An effective means of extending existing user bases, increasing ARPU values, enabling subsequent network evolution, and stabilizing and strengthening existing leadership positions.
WiMAX naturally serves broadband data services, and unlike the previous technologies that provide data value-added services, the nature of network construction must also follow the characteristics of broadband data services. First, capacity has become the main KPI for considering network quality. The construction of macro cells must balance the balance of network capacity and coverage. WiMAX will only stand out in the market competition by providing DSL-like speeds several times higher than HSPA. Secondly, the mainstream business (Internet) and terminal mode (notebook and PC) determine that WiMAX's current business forms are still fixed and nomadic. The specific performance is the discontinuity and unevenness of the business distribution. The deep coverage of hotspots has become the primary consideration in planning. Focusing on these two characteristics of data network construction, ZTE creatively proposed the networking idea of ​​flexible networking. From the two aspects of hybrid networking of macrocells and hierarchical networking of series of cells, the requirements of operators are deeply analyzed. Conduct a program demonstration.
Hybrid networking, tailored to local conditionsFrom the above analysis, one of the characteristics of wireless broadband data networks is that the distribution and development of business needs are geographically uneven, that is, 70% of business needs are concentrated in 30% of geographical areas, such as CBD, residential areas, Hotspots, etc., this 30% of the geographical area is the main source of the operator's entire network profit, we call it the value area, and the other 70% of the area is the non-value area. Taking the HSPA+ site map (yellow dots on behalf of the site) of an operator in Hong Kong as an example, we can clearly draw the above conclusion that 50% of the sites are deployed in the Golden Bowl, which accounts for less than 5% of the total network area. The area is designed to provide an average of 6 Mbps per user to ensure sufficient competitiveness.
Elastic networking to build WiMAX wireless broadband network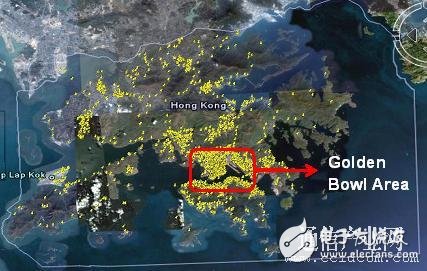
Figure 1 Hong Kong HSPA+ network site distribution
Obviously, the service characteristics of the value area and the non-value area are different. The density of users in the value area is large, the high-end customers gather, and the single-user demand is above the M level. The operator needs to solve the problem of the quality of the Internet, so the large capacity is the core to meet the customer's needs. Elements; non-value areas are sparsely populated, users have relatively low demand for speed, and the key is to solve the problem of being able to access the Internet, so ensuring wide-area coverage is the core element. In order to achieve the overall network planning and investment optimization, it is necessary to achieve the optimal balance of coverage and capacity through 'hybrid networking' for different core needs of value areas and non-value areas.
For the value areas of dense urban and urban areas, we can measure the capacity of the network unit area by the parameter of capacity density. Network capacity density is the ratio of capacity to coverage area. It reflects the user's service experience simulation results more accurately than the simple capacity or coverage indicator. The 2T2R capacity density is higher than 4T4R under the same MIMO multi-antenna technology and channel environment. About 72%, 2T2R per unit area can provide higher average throughput, while also providing higher downstream traffic (by 34.3%) for edge users. It can be seen that in the value area, the 2Tx*2Rx networking can achieve the best balance of capacity and coverage, and meet the key needs of customers for large capacity.
For the non-value areas that are sparsely populated in suburbs and rural areas, the goal of network construction is to maximize coverage, reduce the number of stations, and reduce the overall TCO. Due to the difference in transmit power between the base station and the terminal, the bottleneck limiting the coverage is often the uplink. It turns out that the asymmetric 2Tx/4Rx is used (4 receives a 4.5dB gain with respect to 2, which can reduce the number of stations by 40%) or 4Tx/8Rx. (8 receives 2-3dB gain compared to 4, which can reduce the number of stations by 30%) is the best way to improve the uplink coverage and achieve the balance of uplink and downlink coverage. In addition, solutions that use high-gain terminals and ultra-long coverage are effective ways to improve coverage.
In summary, the hybrid networking not only ensures the large capacity of small cells in the value area, but also enhances the user service experience; and realizes the large coverage of non-value large cells and reduces the demand for TCO reduction, which is the operator's optimization of the entire network planning and The preferred solution for the investment benefit ratio.
Layered architecture, smooth unloadingHybrid networking solves the problem of macrocell capacity and coverage balance. However, how to strengthen the hotspot depth coverage is another issue for the uneven distribution of data services. A layered architecture is the best solution to this problem.
The idea of ​​a layered architecture is similar to the 'heterogeneous network' advocated by the industry. It can also be called a WiMAX homogeneous heterogeneous network. The main idea is that the capacity of the network cannot be carried only by the macro cell. Especially for the large capacity of the hotspot area, the network capacity is uninstalled through the multi-layered network of Micro/Pico/Femto, and can be completed step by step according to the development of the service. . As shown in the figure below, the Micro/Pico/Femto size cells are layered and superimposed to complement each other to construct a flexible network that can flexibly expand.
Elastic networking to build WiMAX wireless broadband network
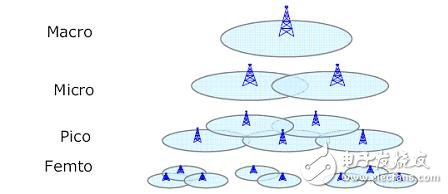
Figure 2 WiMAX layered network
Hierarchical networks have several advantages over traditional macrocell unloading. One is flexible. The imbalance in the development of wireless data network services described above shows that network capacity must not increase evenly across the entire network. In the case of insufficient carrying capacity, Micro/Pico/Femto can see the needles and place them on demand. The size of the cells is flexibly selected according to the traffic density and coverage of the deployment interval. Second, the interference is small, and the transmission power of Micro/Pico/Femto is small. Easy to plan, greatly reduce the interference to the macro cell; Third, the deployment cost is low, as shown in the comparison chart below, it can be seen that the cost of the new Micro/Pico / Femto site is much lower than that of the macro station.
Elastic networking to build WiMAX wireless broadband network
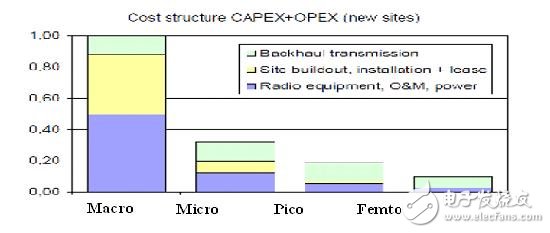
Figure 3 Macro/Micro/Pico/Femto new site cost comparison
Indoors, as the main place of business, is the most important hotspot coverage object, which has caused more and more attention from operators. According to the statistics of Japanese operator NTT DoCoMo, although indoor coverage only accounts for 20% of all coverage areas, more than 70% of data services, especially high-speed data services, occur indoors. The advantages and disadvantages of indoor coverage directly affect operators. Competitiveness. Due to the higher frequency band of WiMAX, compared with 2G/3G networks, indoor coverage has more blind spots and is more difficult to solve by outdoor macro base stations. Considering that indoor vertical capacity density is increased several times or even several times compared with outdoor, and the wireless environment is complex, several Pico base stations can be deployed to fully absorb capacity through each layer, and inter-layer co-frequency multiplexing can achieve stereoscopic coverage of buildings. The purpose of deep coverage.
ZTE is committed to the customized development of serialized WiMAX products, providing 2Tx/2Rx Macro, 2Tx/4Rx Macro, 4Tx/8Rx Macro, Micro, indoor and outdoor Pico and other industry's most complete base station products and end-to-end solutions through hybrid networking. And layered networking helps operators build flexible networks and effectively increase the return on investment of customers.
Guangzhou Winson Information Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.barcodescanner-2d.com