Can ordinary capacitors replace safety capacitors?
Can a safety capacitor be replaced by a regular capacitor? Safety capacitors are specifically designed for applications where they don’t pose an electric shock hazard or compromise personal safety. These capacitors are primarily used in anti-jamming circuits for filtering purposes. Unlike standard capacitors, safety capacitors retain their charge for a longer period after the power source is disconnected. If touched, they could deliver a shock, whereas safety capacitors eliminate this risk. Due to safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) concerns, it's advisable to install a safety capacitor at the power input.
At the AC power input, it’s typical to include three safety capacitors to mitigate conducted EMI. These capacitors are part of the power supply filter and help suppress common mode and differential mode interference.
Y capacitors, which connect between the live and ground lines or neutral and ground lines, are considered safety capacitors. Their placement is crucial to avoid equipment leakage or electrically charging the casing, which could endanger users. These capacitors must have limited capacitance values and high withstand voltages. For instance, in subtropical regions, the earth leakage current shouldn't exceed 0.7 mA, while in temperate zones, it should stay below 0.35 mA. Consequently, the total capacitance of Y capacitors usually doesn't surpass 4700 pF (472). The Y capacitor's capacitance should be controlled to regulate the leakage current and impact on the system’s EMC performance. According to GJB151 standards, the Y capacitor's capacitance shouldn’t exceed 0.1 μF. Additionally, Y capacitors require sufficient safety margins for electrical and mechanical performance to prevent breakdowns or short circuits in extreme conditions. The voltage rating is vital for ensuring personal safety. Notably, Y capacitors intended for safety applications must receive approval from recognized safety inspection agencies. They are often orange or blue and marked with safety certifications like UL or CSA, along with a withstand voltage of AC250V or AC275V. However, their actual DC withstand voltage is much higher, around 5000V or more. Importantly, Y capacitors cannot be substituted with standard capacitors rated at AC250V or DC400V.
X capacitors, placed in parallel between the live and neutral lines, are another type of safety capacitor. Their positioning is equally important and must adhere to safety standards. X capacitors can have a larger capacitance compared to Y capacitors, depending on the application. To prevent the power cord from becoming energized during the charging and discharging cycles of the capacitor, a safety resistor must be connected in parallel. Safety standards dictate that the voltage across the power cord plug (or ground potential) should drop to less than 30% of the original operating voltage within two seconds after unplugging. Like Y capacitors, X capacitors need approval from safety inspection bodies. They are marked with safety certifications and a withstand voltage of AC250V or AC275V, though their actual DC withstand voltage is over 2000V. Using standard capacitors such as AC250V or DC400V in place of X capacitors is not advisable.
In general, X capacitors utilize polyester film capacitors, which are bulkier but allow for high ripple currents. These capacitors have lower internal resistance, enabling them to handle large instantaneous charges and discharges. Standard capacitors typically have lower ripple current ratings and higher internal resistances, making them unsuitable substitutes for X capacitors.




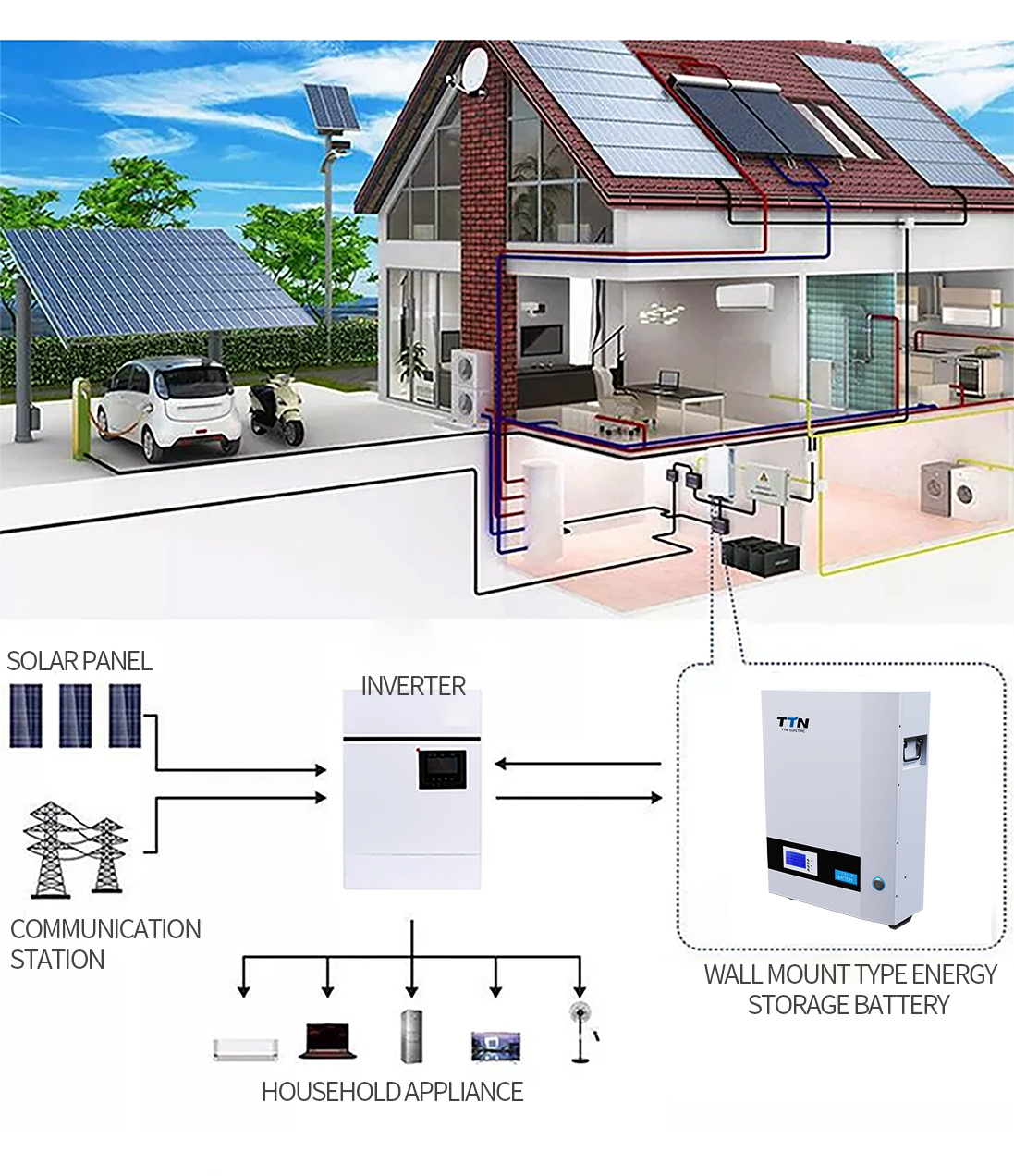


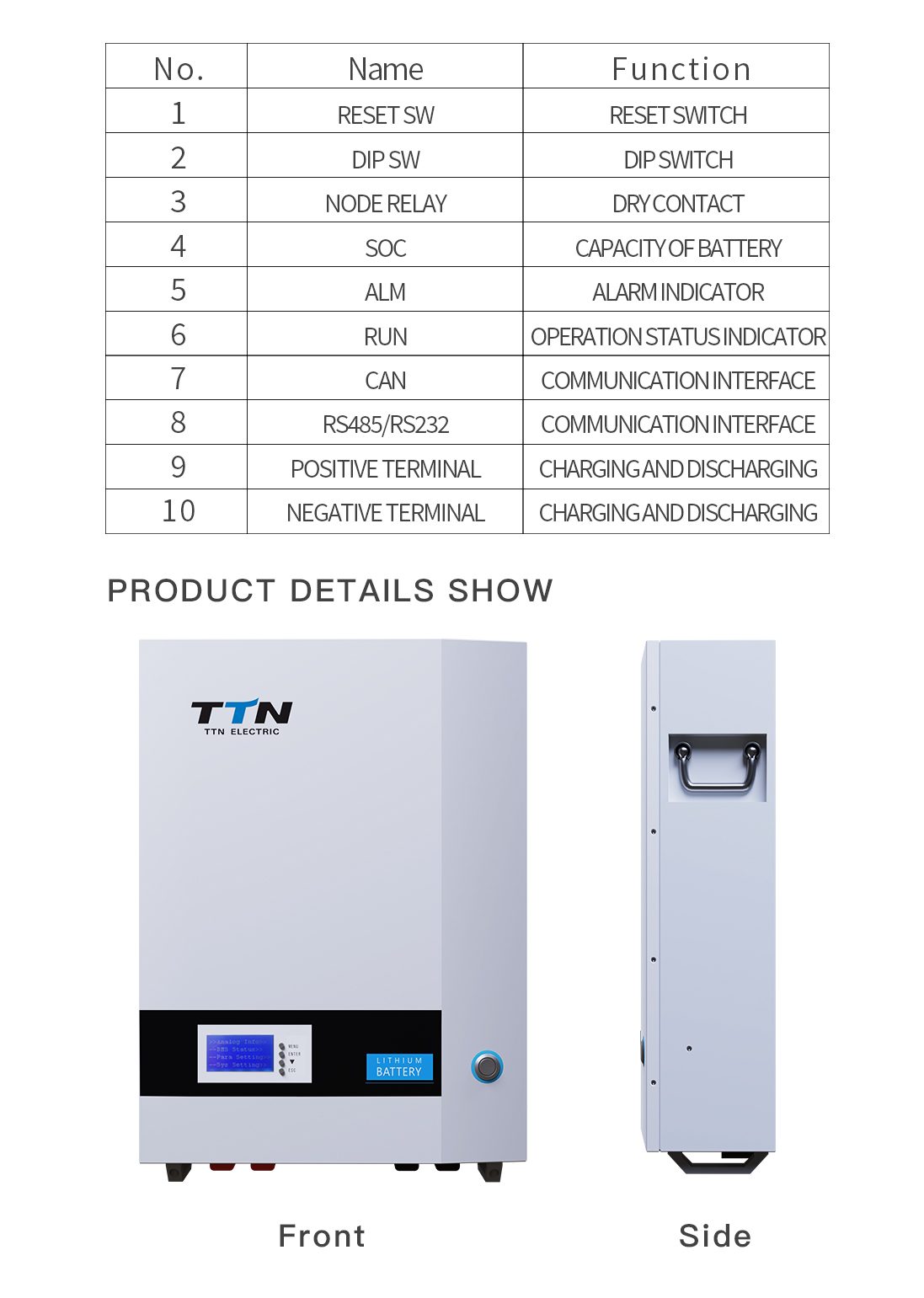




lithium battery
zhejiang ttn electric co.,ltd , https://www.ttnpower.com