Definition and measurement of passband
The passband is used to measure the amplification capability of the amplifier circuit for different frequency signals. Due to the presence of reactive components such as capacitance, inductance, and junction capacitance of the semiconductor device in the amplifier circuit, when the input signal frequency is low or high, the value of the amplification factor decreases and a phase shift occurs. In general, the amplifier circuit is only suitable for amplifying signals in a specific frequency range.
As shown in the figure, the amplitude-frequency characteristic curve of an amplifier circuit.
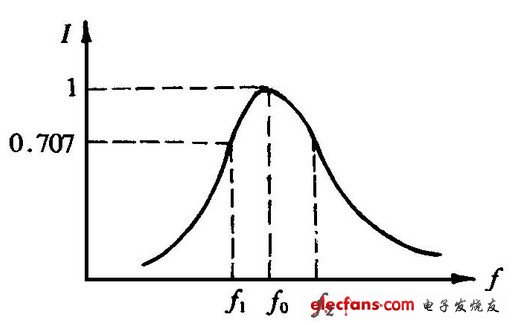
Lower limit cutoff frequency fL: When the signal frequency drops to a certain extent, the value of the amplification factor drops significantly, and the frequency at which the value of the amplification factor is equal to 0.707 is called the lower limit cutoff frequency fL.
Upper limit cutoff frequency fH: When the signal frequency rises to a certain level, the value of the amplification factor will also decrease, and the frequency at which the value of the amplification factor is equal to 0.707 times is referred to as the upper limit cutoff frequency fH.
The passband fbw: the band formed between fL and fH is called the mid-band, or the passband fbw.
Fbw=fH-fL
Or defined as: in the signal transmission system, the signal frequency of the system output signal attenuated by 3dB from the maximum value is the cutoff frequency, the frequency band between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies is called the passband, and the wider the passband is indicated by BW, indicating that the amplification circuit is different. The adaptability of the frequency signal is stronger.
The narrower the passband, the stronger the ability of the circuit to select the center frequency of the passband.
"passband";
Other capacitors
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD , https://www.yzpstcc.com